- The Prohuman
- Posts
- NASA let AI plan a Mars drive
NASA let AI plan a Mars drive
Plus: Inside OpenClaw’s strange early momentum
Hello, Prohuman
Today, we will talk about these stories:
AI just planned a rover route on Mars
A Google engineer crossed a hard line
AI assistants are talking to each other now
Perseverance let AI pick the path
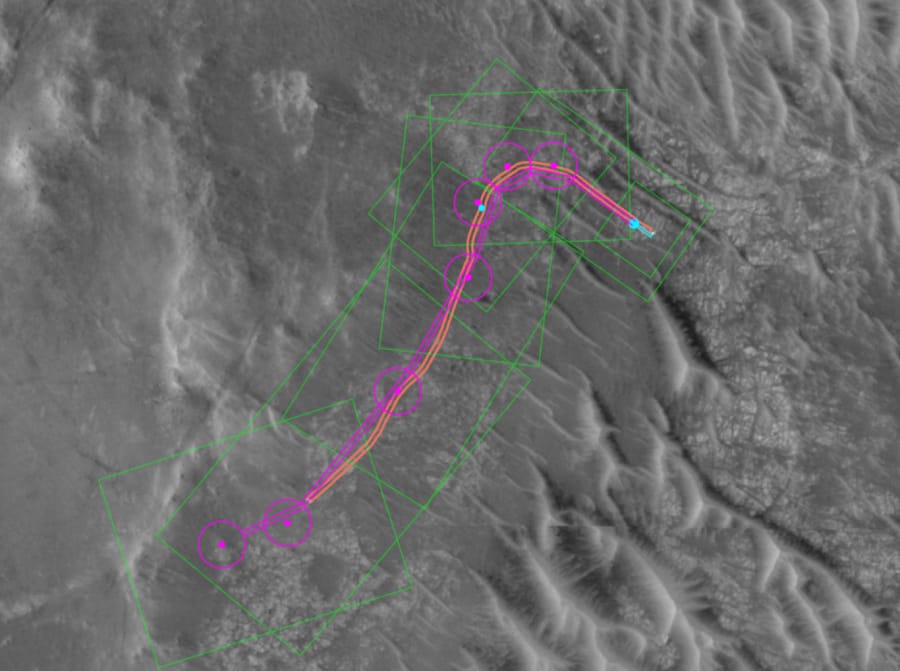
Image Credits: NASA
NASA let AI decide where the rover should drive.
In December 2025, Perseverance completed two Mars drives using AI-generated waypoints instead of routes planned by human operators at JPL.
The system used vision-language models, trained on the same imagery humans use, and sent Perseverance 689 feet one day and 807 feet two days later across the rim of Jezero Crater.
This is not about autonomy hype. It is about shaving hours of human labor from a process constrained by a 140-million-mile delay and brittle planning cycles that top out at 100 meters per segment.
The careful step here matters: the AI’s commands were run through a digital twin checking over 500,000 telemetry variables before anything touched the rover.
If this holds up, rover driving stops being the bottleneck and starts scaling, especially as missions move farther out and operators sleep while machines plan.
It also shows NASA is willing to use modern generative models in live missions, slowly, with guardrails.
The open question is how much judgment NASA is willing to hand over next.
A rare conviction with real consequences

This one ended with a jury verdict.
A former Google engineer, Linwei Ding, was convicted on 14 counts after stealing more than 2,000 pages of confidential AI documents tied to Google’s chips and supercomputer software.
Prosecutors said he downloaded the files days before resigning, while courting investors and working with Chinese companies, telling them he could recreate Google’s AI infrastructure.
What stands out is how concrete this case is: hardware designs, system software, a personal laptop, and a clear timeline.
For years, AI espionage has sounded abstract and political, but this shows how narrow the gap really is between a single employee’s access badge and national security charges filed in a quiet federal courtroom.
Expect more internal controls and quieter paranoia inside big AI labs, especially around chips and interconnects.
This verdict makes it easier for prosecutors to pursue similar cases without being accused of speculation.
The question is how many similar exits never leave this kind of paper trail.
AI assistants just found each other

Image Credits: OpenClaw
AI assistants are now posting to forums.
The open source AI assistant once called Clawdbot, now OpenClaw, has crossed 100,000 GitHub stars in two months and spawned a side project called Moltbook, a social network where AI agents talk to other agents.
These bots check in every four hours, post to Reddit-style “Submolts,” and swap instructions on things like Android automation and webcam analysis.
This matters less because it feels futuristic and more because it exposes how quickly hobbyist tools can drift into shared systems with real behavior and coordination, often before anyone locks them down.
When respected developers like Andrej Karpathy and Simon Willison are openly watching, it signals this is no longer a fringe experiment run on a laptop at 2 a.m. with the screen glowing blue.
The security warnings are serious, and the maintainers keep repeating them, which tells you the risk curve is already steep.
Mainstream use is far off.
What happens when these agents stop feeling experimental to their own builders?
Prohuman team
Covers emerging technology, AI models, and the people building the next layer of the internet. |  Founder |
Writes about how new interfaces, reasoning models, and automation are reshaping human work. |  Founder |
Free Guides
Explore our free guides and products to get into AI and master it.
All of them are free to access and would stay free for you.
Feeling generous?
You know someone who loves breakthroughs as much as you do.
Share The Prohuman it’s how smart people stay one update ahead.